Blog
Mastering the Metering and Mixing of 3M™ Glass Bubbles
Optimize your metering and mixing processes with 3M™ Glass Bubbles.
Learn best practices for handling 3M™ Glass Bubbles to maintain their integrity during mixing, ensuring optimal performance in your final product.
The 3M™ Glass Bubbles Metering and Mixing Guide offers invaluable insights into efficiently handling these innovative materials. Glass bubbles, known for their lightweight and durable properties, require specific techniques for optimal processing. This article highlights the essential considerations for metering and mixing 3M™ Glass Bubbles, helping you enhance product quality and process efficiency.
Table of Contents:
Related 3M™ Glass Bubbles Articles

The Technology Behind Anti-Condensation Paints (Part 1)

3M™ Glass Bubbles and 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres in the EU Ecolabel Framework

Increasing Time Until Condensation: Advanced Applications of 3M™ Glass Bubbles (Part 2)
Understanding 3M™ Glass Bubbles
3M™ Glass Bubbles are hollow, non-porous spheres designed to reduce weight and enhance the properties of end products. Unlike typical mineral fillers, these glass bubbles require specific handling due to their unique physical characteristics.
Processing Considerations
Efficient metering and mixing of 3M™ Glass Bubbles involve several variables. Proper equipment selection and handling techniques are crucial to prevent breakage and ensure uniform distribution.
Weight and Volume
Glass bubbles occupy more space than traditional fillers, affecting equipment capacity and sensitivity. This requires adjustments in handling and processing equipment to accommodate the unique properties of glass bubbles.
Handling Techniques
Proper handling begins with recognizing that glass bubbles can break under compression, shear, and impact. Balancing microsphere crush strength with equipment choice is vital to prevent breakage during processing.
Hoppers and Hopper Design
Day Hoppers and Weigh Hoppers
In high-volume operations, a vacuum transfer system loads bubbles into a day hopper, which feeds weigh hoppers throughout the work period. For smaller operations, a single hopper can serve both purposes, streamlining the process.
Hopper Design and Flow
Proper hopper design is critical for maintaining a consistent flow of glass bubbles into the metering device.
- Symmetrical Hoppers: These can create discharge problems like bridging and rat holing.
- Asymmetrical Hoppers: Featuring steep sides and offset discharge points, these designs enhance flow and reduce dust generation.
Hopper Design and Flow
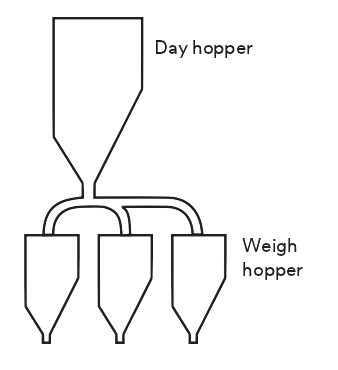
Day Hoppers and Weigh Hoppers
Hopper Design and Flow
Proper hopper design is critical for maintaining a consistent flow of glass bubbles into the metering device.
- Symmetrical Hoppers: These can create discharge problems like bridging and rat holing.
- Asymmetrical Hoppers: Featuring steep sides and offset discharge points, these designs enhance flow and reduce dust generation.
Metering, Feeding, and Mixing
Metering and Feeding Devices
The meter/feeder device controls the flow of glass bubbles from the hopper into the process. Gravimetric loss-in-weight feeders and load cells are common devices used to ensure accurate metering.
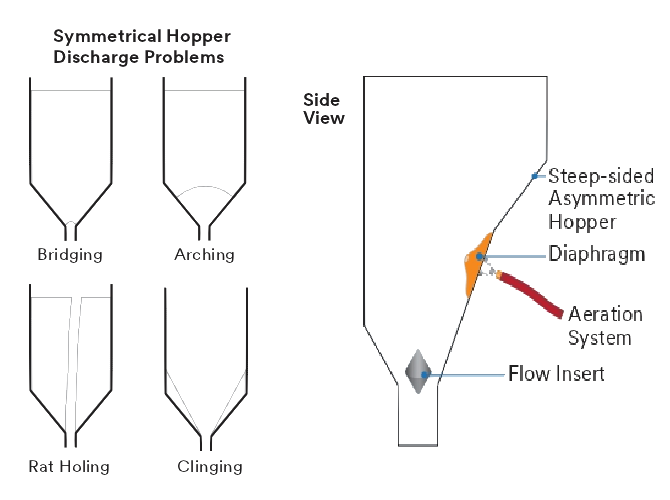
Symmetrical hopper discharge problems like bridging and rat holing. Asymmetrical hopper design with steep sides and offset discharge.
Mixing and Compounding Techniques
To minimize bubble breakage during mixing:
- Introduce a steady or pulsed flow of bubbles directly into the liquid vortex from above.
- Add bubbles as late as possible in the mixing process to reduce exposure to agitation.
Recommended Mixers:
- Anchor
- Planetary
- Double Planetary
- Propeller
- Pitched Blade
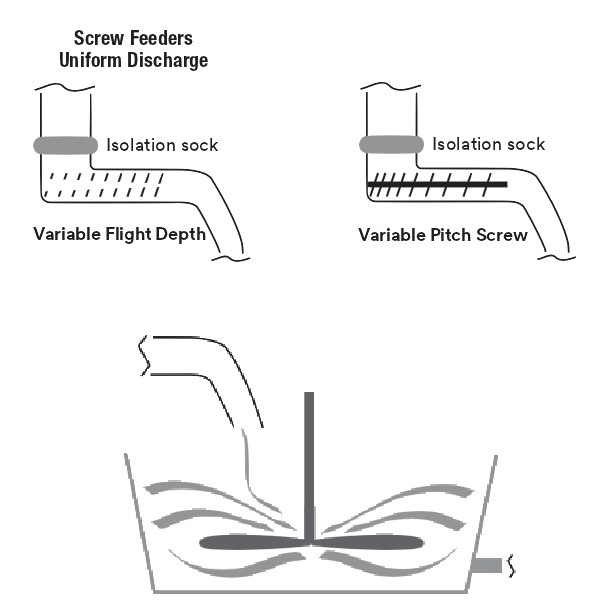
Transfer Mixers
Mixing and Compounding Techniques
To minimize bubble breakage during mixing:
- Introduce a steady or pulsed flow of bubbles directly into the liquid vortex from above.
- Add bubbles as late as possible in the mixing process to reduce exposure to agitation.
Recommended Mixers:
- Anchor
- Planetary
- Double Planetary
- Propeller
- Pitched Blade

Transfer Mixers
Pumping Guidelines
Glass bubbles can be pumped in dry or wet forms. Double diaphragm pumps and peristaltic pumps are preferred, as they minimize damage to the bubbles. Avoid centrifugal, gear,lobe, and progressive cavity pumps.
Request the Full Guide
For detailed instructions and further support, request the complete 3M™ Glass Bubbles Metering and Mixing Guide. This comprehensive guide provides in-depth information to optimize your processes and achieve the best results.
Optimize your paint formulations today!
You might also be interested in...

Increasing Time Until Condensation: Advanced Applications of 3M™ Glass Bubbles (Part 2)
You might also be interested in...








