Blog
Unlocking the Potential of Functional Fillers in Waterborne, UV-Curable Coatings
Optimize your waterborne, UV-curable coatings with functional fillers.
Discover how innovative functional fillers like 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres and nepheline syenite can enhance your waterborne UV-curable coatings.
In the evolving landscape of industrial coatings, functional fillers like 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres and silica matting agents are playing a crucial role. These materials are being integrated into waterborne, UV-curable polyurethane dispersions to enhance properties such as matting efficiency, scratch resistance, and viscosity control. This guide explores the benefits and applications of these functional fillers, offering insights into achieving high-performance coatings with both decorativeand functional finishes.
Table of Contents:
Related 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres Articles

3M™ Glass Bubbles and 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres in the EU Ecolabel Framework

Unlocking the Potential of Functional Fillers in Waterborne, UV-Curable Coatings

Enhancing Paints & Coatings with 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres
Introduction to Functional Fillers
Functional fillers such as 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres and silica matting agents have become essential in formulating waterborne, UV-curable coatings. These fillers not only enhance the performance of the coatings but also contribute to achieving desired aesthetic attributes. This article delves into how these fillers are evaluated for their effects on properties like matting efficiency, scratch resistance, and viscosity control.
Experimental Methods and Materials
A basic, clear, UV-curable polyurethane dispersion formulation was used as a starting point for all material evaluations. The formulation included UV-curable PUD resin, defoamer, wetting agent, dispersant, rheology modifier, matting agent/filler, photoinitiator, and deionized water. The materials were mixed using a 1.5” Cowles blade and cured using a Fusion Light Hammer® 6 unit with a mercury vapor bulb.
Key Findings and Results
Matting Efficiency
The study found that silica matting agents were highly effective, significantly reducing gloss at low loadings (1-5% by weight). In contrast, 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres and nepheline syenite required higher loadings (20-25%) to achieve similar matting effects.
Viscosity
3M™ Ceramic Microspheres showed minimal impact on viscosity at high loadings (>20%), while nepheline syenite and some silicas significantly increased viscosity, potentially requiring additional dilution for application.
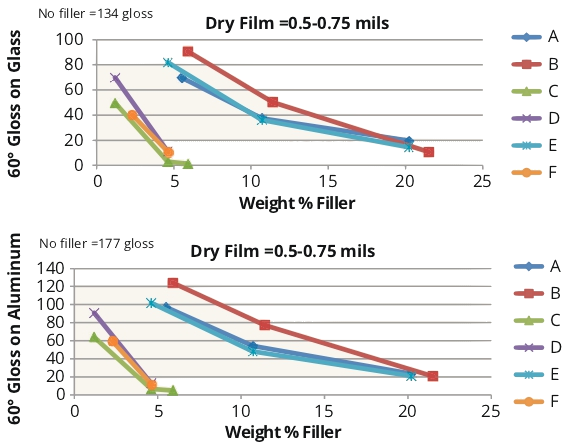
Graph showing matting efficiency of various fillers in waterborne UV-curable coatings.
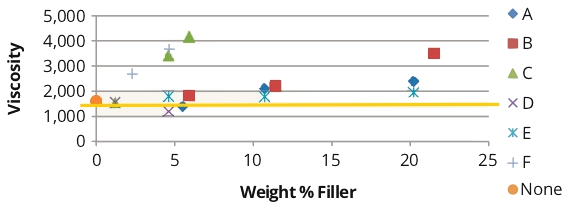
Graph depicting the viscosity profiles of different fillers in waterborne UV-curable coatings.
Clarity and Haze
As filler loading increased and gloss levels decreased, clarity also decreased. However, the visual appearance on wood panels remained acceptable, maintaining visible grain.
Scratch Resistance
3M™ Ceramic Microspheres offered consistent performance, with minimal change in appearance after 200 cycles of scratch testing. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high durability.
Abrasion Resistance
All systems performed well after 500 cycles of Taber abrasion, with no wear through and minimal weight loss, highlighting their durability.
Cost/Value Benefits
Silica matting agents, while effective at low loadings, had a higher cost structure. 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres and nepheline syenite offered potential cost benefits at higher loadings, making them viable alternatives for formulators.

Visual appearance of different fillers on oak boards in UV-curable clearcoats.
Optimized Formulation Example
An optimized formulation using 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres demonstrated superior matting efficiency and performance in waterborne, UV-curable coatings. This formulation provides a practical example of how to achieve high-performance coatings with functionalfillers.
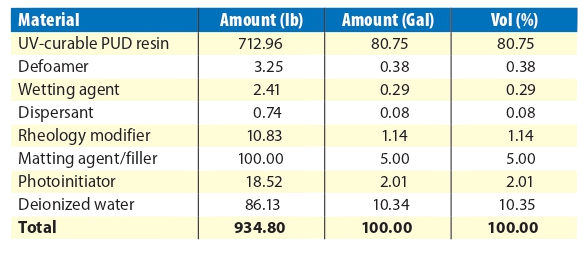
Table showing the basic UV-curable waterborne starting-point formulation.
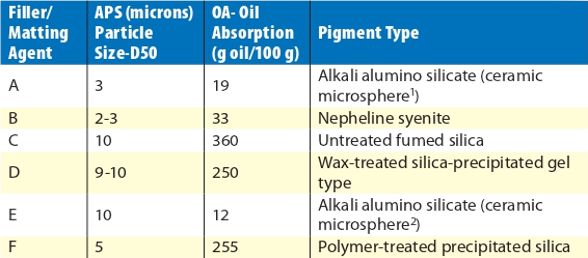
Table listing the basic properties of the fillers evaluated
An optimized waterborne, UV-curable coating formulation was developed using 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres. This formulation demonstrated superior matting efficiency, enhanced performance, and improved scratch resistance, outperforming many conventional coatings.
The Full Guide
For a detailed understanding of how 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres and other functional fillers can enhance your waterborne, UV-curable coatings formulations, and to see the specific information, request to download the comprehensive document. It provides a thorough analysis of these materials, offering you the tools to optimize your products effectively.
Conclusion
Integrating functional fillers like 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres and silica matting agents into waterborne, UV-curable coatings presents a highly effective solution for achieving high-performance and aesthetically pleasing finishes. These fillers enhance properties such as matting efficiency, scratch resistance, and viscosity control, making them ideal for industrial applications.
Interested in optimizing your waterborne, UV-curable coatings formulations?Request a sample today and take the first step towards creating superior, high-performance coatings with functional fillers like 3M™ Ceramic Microspheres!
Optimize your paint formulations today!
You might also be interested in...

Increasing Time Until Condensation: Advanced Applications of 3M™ Glass Bubbles (Part 2)
You might also be interested in...








