{{placeholder content=’e3ticml6eV9kY19wb3N0X3RpdGxlfX0=’}}
{{placeholder content=’e3ticml6eV9kY19wb3N0X2V4Y2VycHR9fQ==’}}
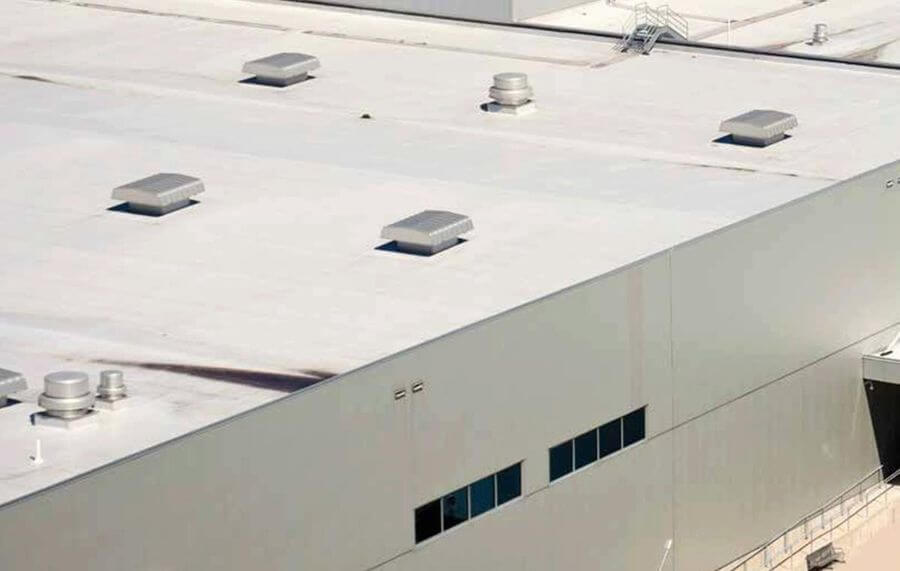
Pioneering Sustainable Building Solutions
In the ever-evolving world of sustainable construction, 3M Glass Bubbles have emerged as a pivotal innovation. These unique materials are redefining the efficiency of roof coatings by significantly boosting their solar reflectance. This article delves into how 3M Glass Bubbles are offering a ground breaking, energy-saving alternative to conventional materials in the building industry.
Understanding the Role of Solar Reflectance
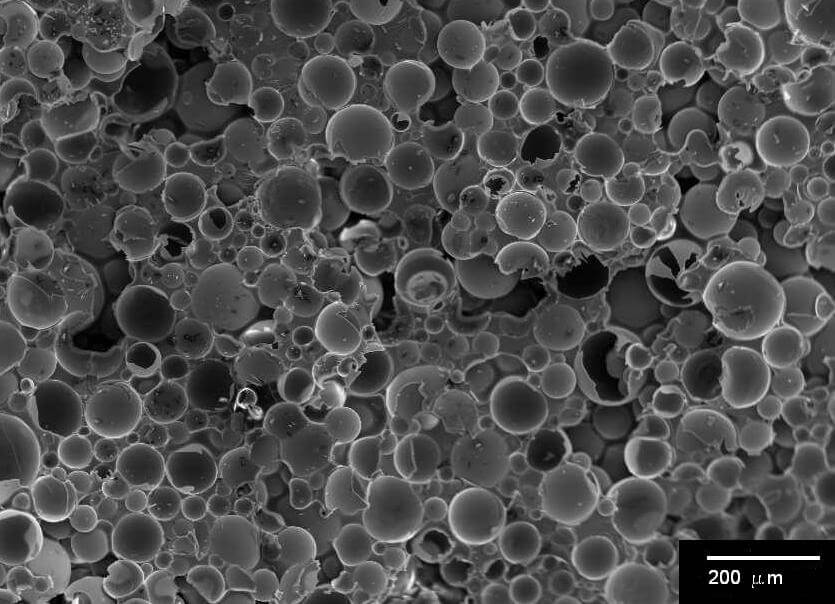
Solar reflectance is crucial in the effectiveness of ‘cool roof’ technologies, where ideal coatings reflect over 80% of solar energy. This high reflectance rate is essential as it minimizes solar energy absorption, reducing the dependency on air conditioning and thereby cutting down on energy costs. Traditionally, materials like titanium dioxide have been used to reflect solar radiation. However, 3M Glass Bubbles stand out as a superior option due to their unique ability to scatter light, attributed to their hollow structure.

Total Solar Reflectance (TSR) Enhancement
Boosting Cooling Efficiency
Beyond TSR, 3M Glass Bubbles significantly contribute to the thermal diffusivity of roof coatings. Experimental data using coatings on aluminum panels indicate
that the inclusion of these glass bubbles markedly reduces heat transfer, a direct benefit of their high TSR.
Advantages Over Traditional Fillers
Lightweight and Strong
3M Glass Bubbles enhance roof coatings with their low density and high crush strength, making application easier and more durable.
Improved Flow Characteristics
The spherical nature of these microspheres leads to lower viscosity in coatings, simplifying the application process.
Efficient Binder Usage
The unique surface area to volume ratio of 3M Glass Bubbles minimizes binder requirements, resulting in coatings with higher solid content and reduced shrinkage.
Practical Applications in the Construction Industry
The use of 3M Glass Bubbles in roof coatings is not limited to energy savings. Their enhanced solar reflectance and thermal properties also play a vital role in extending the durability and efficiency of roofing systems, particularly beneficial in areas with high solar irradiance.
A Step Towards Greener Construction
3M Glass Bubbles are more than an advancement in roofing materials; they represent a significant stride towards environmentally friendly construction practices. Their diverse benefits in terms of solar reflectance, strength, and ease of application make them an exemplary choice for progressive, energy-efficient roofing solutions.
Learn More About 3M Glass Bubbles
{{ brizy_dc_global_blocks position=’bottom’ }}